Saturday, May 25, 2019
Weekly Indicators for May 20 - 24 at Seeking Alpha
- by New Deal democrat
My Weekly Indicators post is up at Seeking Alpha.
The big contradiction between what the yield curve is forecasting, and what most of the rest of the long leading indicators are forecasting, continues. Meanwhile Trump’s tariff “policies” are creating chaos in other sectors.
As usual, clicking over and reading should not only bring you up to date, but helps reward me with a penny or two for my work.
Friday, May 24, 2019
Economic indicator death match update: either bonds or housing sales are giving a false signal
- by New Deal democrat
Yesterday featured the week’s sole important economic release: new home sales. But first, let’s update the inverted bond yield curve, which got more dramatic yesterday. The below graph compares the depth of the inversion yesterday (bottom) with March of 2007 (top):
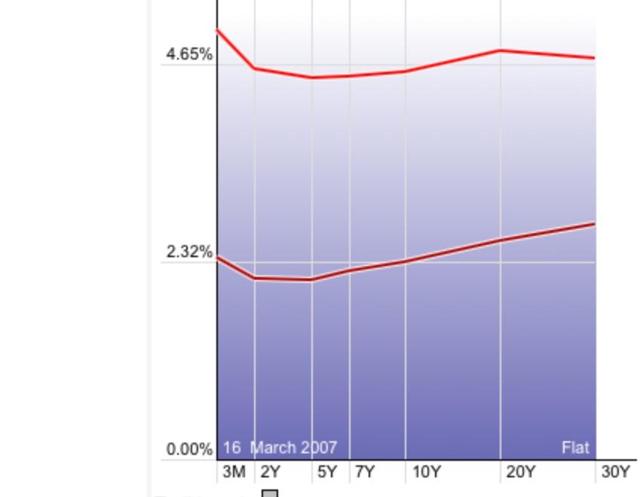
With the sole exception of the 2 vs. 10 year spread, the yield curve is virtually screaming oncoming recession at this point.
Now let’s turn to new home sales. As a refresher, new home sales are the most leading of any housing series, but they are extremely volatile and heavily revised. Yesterday they were reported down -6.9% m/m for April, but that wasn’t the important news, because March was revised higher to a new expansion high. As the below graph shows, only once in the past 50+ years have new home sales made their cycle low *before* the onset of recession - in 2000:
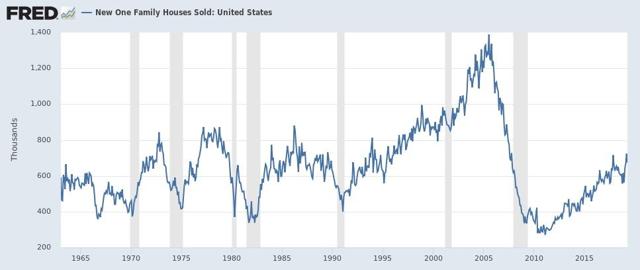
So, while it’s only one data series, just going by past history, yesterday’s report very likely negatives any recession in the near future, completely contradicting the bond yield curve.
Of course, mortgage applications, and new home sales, have rebounded this year because interest rates have fallen from a peak of close to 5% last November to 4.1% this week. So in the below two graphs, I show new home sales (blue) vs. mortgage rates (red, right scale) since the latter series was started in 1971:
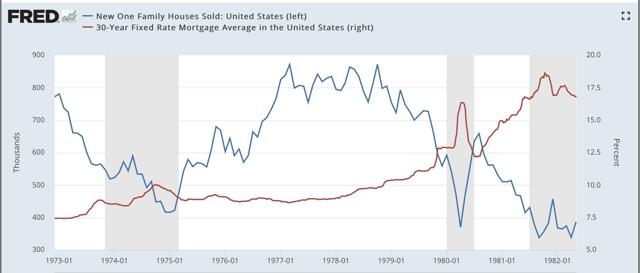
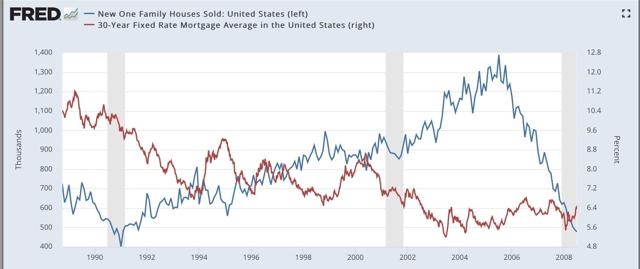
Mortgage rates didn’t decline at all prior to the 1980 recession, and declined only trivially in the month before the onset of the 1970 and 1981 recessions. They declined more significantly — -0.6%, -1.7%, and -0.8% — before the onset of the 1991, 2001, and 2008 recessions. In the cases of both the 1991 and 2008 recessions, housing still declined in part due to oil price shocks and in 2008 the unwinding of leverage in housing and the mortgage markets. The 2001 recession, by contrast, was a producer-led downturn, as the dotcom bubble imploded, so the mild upturn in housing was not enough to overcome it. Housing did turn down *during* the 2001 recession, as people got laid off, but did not match its 2000 low.
Now here is an update of the same data for this expansion:
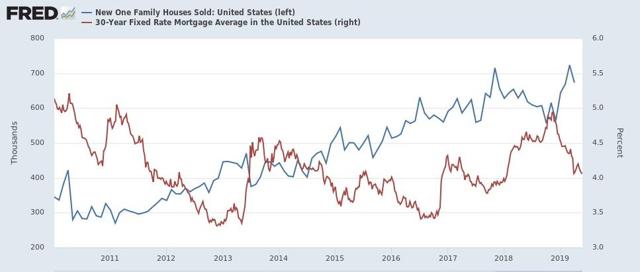
The bounce in new home sales in the past several months has been much stronger than that of 2000.
The big fundamental question in the economy right now is whether the upturn in housing will be enough to overcome the downturn in corporate profits for the past two quarters. In short, one of these two powerful economic indicators is giving a false signal.
Thursday, May 23, 2019
Initial claims, temporary staffing point to weaker May jobs report
- by New Deal democrat
As I’ve noted a few times recently, I’m paying additional attention to the weekly jobless claims numbers, partly because I suspected that the late Easter this year resulted in some residual seasonality (which I think has been demonstrated), and partly because if my slowdown forecast is correct, it ought to start showing up there.
The initial claims report this morning covered the week during which the BLS surveyed employers for the May jobs report coming out in two weeks. In the four weeks that coincided with the April report, initial claims made new 49 year lows, averaging 201,500. In the past five weeks that will coincide with the May report, the average has been 221,500.
So, while this isn’t precisely on point, here’s a graph of the four week moving average of claims (blue, left scale) vs. the unemployment rate (red, right scale):
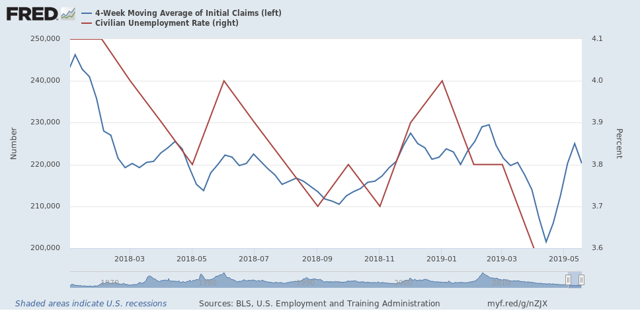
I don’t think it was a coincidence that the unemployment rate fell to a 50 year low during the four week period that initial claims made 49 year lows. And I strongly suspect that the June report will take that back, with an unemployment rate of 3.8% +/-0.1%.
If that happens, it will be significant, because a 3.8% unemployment rate would be exactly what the rate was 12 months previously. And a YoY unemployment rate that has not improved has only happened once during this expansion (September 2016, right before the election).
Further, at the moment initial claims are higher YoY:
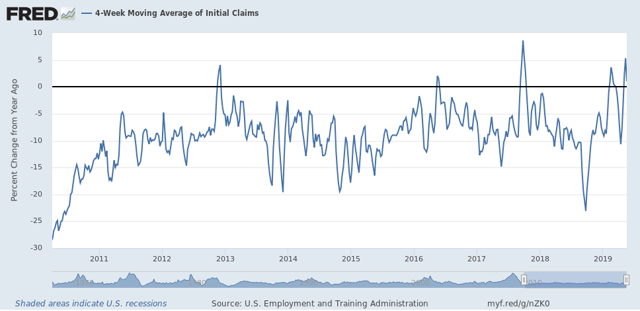
Even if they continue at the 210-212,000 range for the next few weeks, that’s still only about a 4% improvement from a year ago.
Bottom line: unless jobless claims continue to fall in the weeks ahead, they are consistent with a slowdown.
And while I’m at it, another leading sector - temporary jobs - continues to show weakness as reported in the weekly American Staffing Association’s Index:
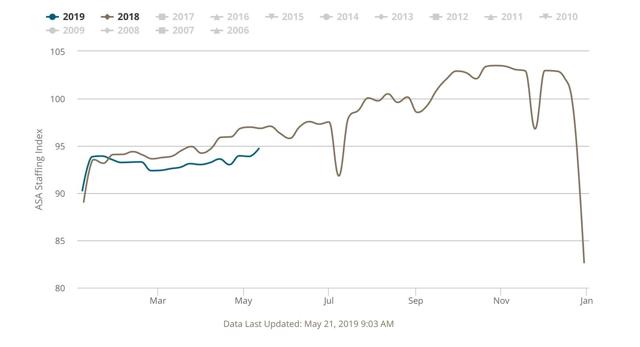
The four week average of the index is -2.9% YoY, the worst showing since the 2015-16 slowdown.
I was surprised by the strong +12,000 temporary jobs number in the April jobs report. I am expecting either that to get revised downward, or a poorer comparison when May’s report comes out, or both.
In short, the weekly data so far this month is consistent with an oncoming slowdown in employment gains. We’ll see in two weeks.
Wednesday, May 22, 2019
A comment about the economy and the 2020 election
- by New Deal democrat
Recently I’ve seen a bunch of takes to the effect that “the economy is doing great, and therefore it is likely that Donald Trump will be re-elected.” In my opinion that fear is overblown for three important reasons.
The fist, least noteworthy reason, is that there is still a lot of time between now and the election. As I noted Monday, many - but not all - models of the economy indicate that a recession is likely between now and then, for reasons having nothing to do with the age of the expansion. Needless to say, a recession in 2020 would not bode well for either Trump or the GOP.
Secondly, consider what economic interventions Trump and the GOP have made since they inherited the economy from Obama. There have been three:
1. They passed a tax cut that lopsidedly favored the wealthy and corporations, that has generated zero acclaim from the middle and working classes - and with the decrease in tax refunds, may have generated net negative feelings.
2. Trump has started several trade wars that are proving unpopular, partly because they mainly have hurt portions of his own base, partly because they are resulting in net higher prices to consumers that may be getting noticed, and partly because negatively affected businesses may start laying off workers.
3. Trump is held responsible for the government shutdown that resulted in a mini-recession.
In short, it’s not clear to say the least that the public at large would give Trump credit for an economy that he mainly inherited from Obama and as to which his known interventions have been received negatively.
Finally, and most notably, the example of the Bush vs. Gore 2000 election strongly cuts against Trump. As I wrote in 2016, all of the fundamentals-based election models, such as the “bread and peace” model, or models based on the unemployment rate or on consumer income and spending, indicated that Gore should have won by nearly a landslide, on the order of 55%-45%, as shown in the graph below:
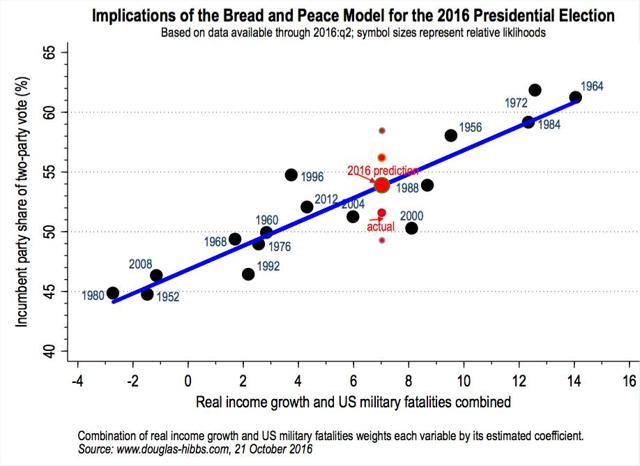
Instead, Gore won the popular vote by only 0.5%, despite being able to run on both peace and prosperity - the biggest outlier of the entire series going back to 1952.
Two big factors held Gore back: first, the economic expansion had gone on for nearly 10 years, and at some point the public takes it for granted, or in other words, “so what have you done for me lately?” Second, as his Vice President, Gore was stained by Bill Clinton’s slimy personal life.
Both of the factors that worked against Gore in 2000 are likely to work against Trump in 2020: if the economy remains in expansion, the public will probably take it for granted; and Trump’s pervasive sliminess, both public and private, will work against him. In short, Trump is likely to underperform compared with the fundamentals even more than did Gore.
While the example of 2016 certainly means that the 2020 election is another “all hands on deck” moment for Democrats, and nothing should be taken for granted, even if the economy remains in expansion as it is now I do not think that means Trump wins the election.
San Francisco Fed: ease of finding a new job is driving improved labor force participation
- by New Deal democrat
This is a surprising result that is worth noting: the San Francisco Fed found that the increase in prime age labor force participation in the past five years has not been due to new people being drawn into the labor force, but rather by a very large decrease in people leaving it:
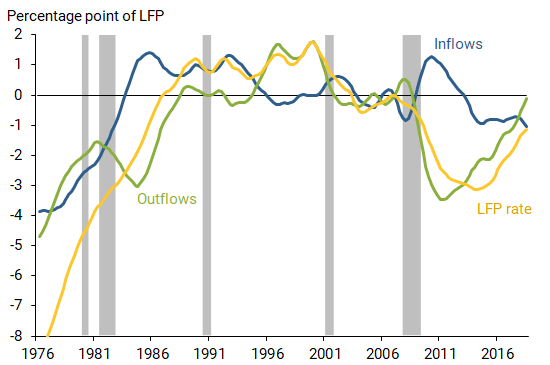
[Note: keep in mind that prior to the early 1990s, both inflows and outflows are increasing due to the secular trend of women entering the workforce.]
Why is this surprising? Because you would think that increased wages would draw people on the sidelines into the workforce. This is something I’ve looked at a few times in the past several years, and the pattern has been clear:
1. The unemployment rate declines
2. Once the unemployment rate declines enough, the decline in labor force participation decelerates, but nevertheless continues.
3. Average hourly wage growth starts to improve.
4. Labor force participation starts to increase.
Here’s a graph showing this relationship since 1994:
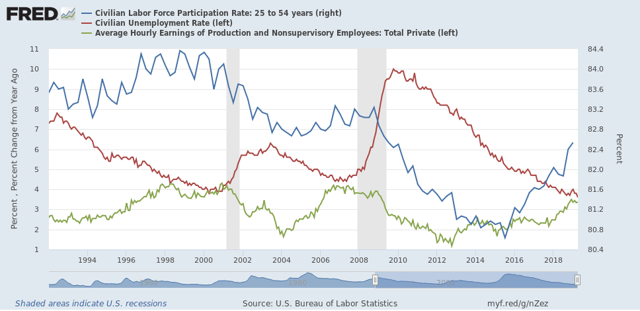
The San Francisco Fed says that the reason for the big decline in outflows has been the ease of finding a new job, although that appears to be speculation. It might be that improved wage growth is something that is noticeable to people already in the labor force, rather than those presently outside of it.
Anyway, a counter-intuitive result worth noting.
Tuesday, May 21, 2019
Yes, Virginia, the government shutdown really did cause a mini-recession
- by New Deal democrat
For the past several months, I have been pounding on the idea that the government shutdown, during which 800,000 jobholders were temporarily laid off without pay, had a much bigger impact on the economy than was originally thought.
This morning we get the following graph from Bank of America Merrill Lynch, which speaks for itself:
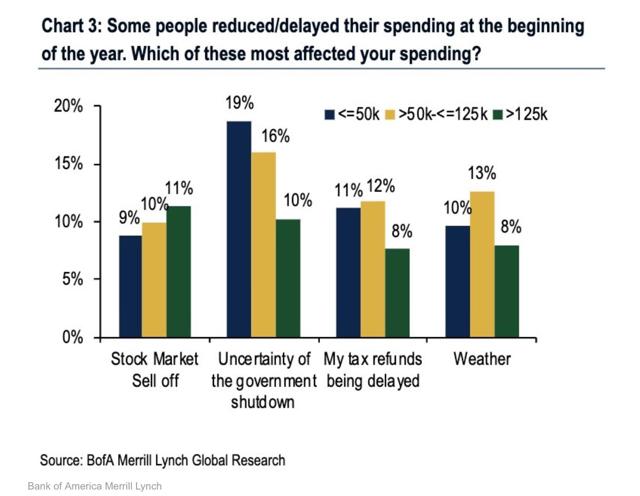
One of the most important insights from behavioral economics is that losses have an outsized effect on behavior compared to gains, usually on the order of 2 to 1. In the case of the government shutdown, about 0.5% of the workforce went without pay for about 45 days. Using the 2:1 ratio, that would translate into a -1% deadweight loss to the economy during that time.
Of course, the workers got back pay when the government reopened - but if the 2:1 ratio holds, there wouldn’t be an equivalent “kick” from renewed spending. Which seems to have been the case, since the March +1.3% rebound in real retail sales didn’t make up for the -1.6% decline in December.
Monday, May 20, 2019
Twelve Big Picture bullet points on the economy
- by New Deal democrat
It’s a really slow week for economic data. Really the only important report is new home sales, which will be released Thursday.
I’ve been working on a few things, but they are really information-dense and time-consuming to organize, and because they deal with how long leading indicators interact with one another, I’ll probably post them on Seeking Alpha.
So in the meantime, let me give you a few hopefully pithy Big Picture observations.
1. Virtually every economic model that relies upon the yield curve is forecasting recession to happen sometime in 2020.
2. The few economic models that don’t rely upon the yield curve suggest a recession *could* happen later this year.
2. The few economic models that don’t rely upon the yield curve suggest a recession *could* happen later this year.
3. If we use a “fundamentals” based model that doesn’t rely on financial conditions like interest rates (“real” corporate profits, housing, and cars), the important data is deteriorating, but not enough at this point to forecast recession vs. slowdown.
4. All of these models seem to have a shortcoming in that they rely too heavily on monetary and interest rate policy, and do not adequately account for fiscal policy, like stimulus. Thus all of them “forecast” a recession in 1966-67 that didn’t happen!
5. The reason no recession happened in 1966-67 was LBJ’s “guns and butter” fiscal policy of Vietnam War military spending + domestic Great Society spending, which increased the budget deficit by 500% (!) and helped keep industrial production from declining.
6. The stimulus passed by the Congress at the end of 2016 is much smaller, amounting to only a 50% increase in the deficit. It is also much smaller than either Reagan’s or W’s tax cut stimulus.
7. In any event, the stimulative effect is estimated to end by the end of this year.
8. Contrarily, Trump’s tariffs amount to large, regressive sales tax increases.
9. Which means that, if things don’t change, by next year fiscal policy will be a net drag on the economy.
10. The question remains whether the positive effect of lower mortgage rates can overcome that drag, and the drag of higher short term interest rates.
11. In the meantime, every metric I use indicates that job gains are set to decrease substantially starting more or less right now. The UCLA forecast puts this figure at about 160,000 a month for this year.
12. Needless to say, if a recession happens by the end of 2020, especially if Trump’s tariffs play an important role, fundamentals-based Presidential election models do not bode well for Trump or the GOP.
Sunday, May 19, 2019
Nancy Pelosi is an able tactician, but a poor strategist. She will not save the Republic
- by New Deal democrat
A couple of years ago I read Andrew Roberts’ tome on Napoleon. As a schoolboy, Napoleon voraciously inhaled everything he could read about military conflict, including several then-recent books suggesting novel tactics. As a young general, he implemented those tactics to brilliant effect, winning almost every big battle he fought.
But if he was a masterful tactician, he was a so-so strategist. His strategy essentially consisted of:
1. Invade neighbor’s country.
2. Win all the big battles.
3. Occupy his capital.
4. Accept large indemnities, and territorial and political concessions, in return for going home.
By the time he got to the last big continental power, Russia, Tsar Alexander and his generals had thoroughly analyzed Napoleon’s style. So they employed a colossal, masterful rope-a-dope strategy in which they retreated after every battle was started, denying him his decisive big victories while drawing him ever deeper into Russia’s heartland - ultimately 1000 miles. The tsar even allowed him to occupy Russia’s “old capital” of Moscow, and set it afire so that Napoleon could not use it to provision him during the winter. Then he simply ignored Napoleon’s entreaties to negotiate step #4. By the time Napoleon realized the tsar was simply going to refuse to capitulate, it was too late, and Napoleon lost over half a million men in the ensuing retreat through the brutal winter back to his nearest supply lines in Poland. Napoleon was fatally wounded, and Tsar Alexander’s men harried his retreat all the way back across Europe. Three years later, Russian troops occupied Paris.
Okay, so I’m not tarring Nancy Pelosi as making Napoleonic mistakes. But there is a comparison, because while Pelosi is a very able tactician, her excessive caution makes her a poor strategist.
Take the government shutdown. Common wisdom is, Pelosi won that battle. But look what was “accomplished:” in return for a government shutdown for about 45 days, with 800,000 federal workers furloughed without pay, causing an actual downturn in economic activity I’ve called a “mini-recession:”
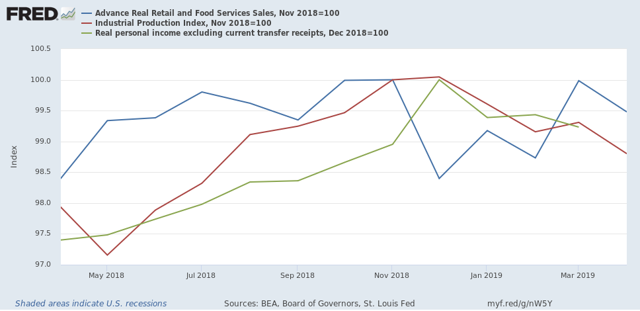
here’s what Pelosi got. Instead of giving Trump $7 billion for his “wall,” she gave him $2 billion. Which by the way hasn’t been spent, and which caused him to declare a “state of emergency” which hasn’t even been passed on by a US District level Court yet. In other words, all of that for about 0.5% of the federal budget. In return for which, the President has so far gotten away with usurping a core area of Congressional responsibility.
Or, even more bluntly, a tactical victory but a strategic defeat.
Pelosi is playing the same tactical game when it comes to impeachment. According to the Chicago Tribune,
Pelosi has repeatedly warned that pursuing impeachment could hurt Democrats’ electoral chances in 2020.
Instead, Democrats should focus on building their majority in the House and winning back the White House and a Senate majority in the 2020 election, Pelosi said. And where they can, Democrats should work with the Trump administration on policies, such as lowering prescription drug prices and investing in infrastructure, that will benefit the American people, she said....
“The urgency to protect the integrity of our democracy is there,” Pelosi said.The answer? “Just win big, baby,” the speaker said.
In other words, the answer to Donald Trump is a democratic victory in 2020 which will enable democrats to pass their agenda (how to deal with the Senate filibuster, assuming the democrats pick up 3 Senate seats, she doesn’t say).
Throughout her career, Pelosi has always accepted polls as gospel, and refused to see that action might *move* the polls. If the House were to impeach Trump, the publicity surrounding the hearings might create a bigger groundswell for conviction. And even if the Senate refused to convict, the groundwork would have been laid that actions such as Trump’s were unacceptable.
Instead, if Pelosi’s path is followed, in the meantime here’s what will have happened:
So, if Pelosi prevails, we will simply accept permanent damage to the US’s Constitutional fabric in return for the temporary ability to maybe get some things done in 2021. As someone else has pointed out, without Congressional action Mueller’s report reads like a blueprint for how to establish corrupt autocratic rule by, say, a President Tom Cotton. And, make no mistake, it will be followed.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)